Next: What Is the Difference Between a Circuit Breaker and a Main Switch Disconnector?

Understanding the fundamental differences between ELCB vs RCCB is crucial for electrical engineers, procurement managers, and industrial buyers making informed decisions about earth leakage protection systems. While both devices serve the critical purpose of preventing electrical shock and fire hazards in residential, commercial, and industrial systems, their operating principles, reliability, and compliance with modern safety standards differ significantly.
The choice between ELCB (Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker) and RCCB (Residual Current Circuit Breaker) affects not only electrical safety compliance but also long-term system reliability and maintenance requirements. As electrical safety standards evolve, understanding why modern installations favor RCCBs over ELCBs becomes essential for procurement decisions and retrofit planning.
Common questions from industry professionals include: Which is better RCCB or ELCB?, Why is ELCB no longer used?, and Can I replace ELCB with RCCB? This comprehensive guide addresses these concerns while providing practical guidance for B2B buyers and electrical system designers.
Key Insight: RCCBs have largely replaced ELCBs in modern electrical installations due to superior reliability, sensitivity, and compliance with current IEC safety standards.
The ELCB (Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker) is a voltage-operated protective device designed to detect earth leakage through voltage imbalance monitoring. ELCBs operate by sensing voltage differences between the earth wire and ground, tripping when the detected voltage exceeds predetermined thresholds, typically between 50V to 100V.
In contrast, the RCCB (Residual Current Circuit Breaker), also known as a residual current device (RCD), is a current-operated protective device that detects earth leakage through residual current monitoring. RCCBs continuously monitor the current balance between live and neutral conductors, tripping instantly when imbalances indicate earth leakage currents that could pose safety risks.
The fundamental distinction lies in their detection methods: ELCBs monitor voltage variations while RCCBs monitor current imbalances. This difference in operating principles explains why RCCBs have replaced ELCBs in modern electrical safety standards, offering superior sensitivity and reliability in earth leakage protection applications.
Both devices serve the critical function of earth leakage protection, preventing electrical shock hazards and reducing fire risks caused by earth fault currents. However, their effectiveness, reliability, and compliance with modern safety standards vary significantly, influencing their suitability for contemporary electrical installations.
Learn More:
Understanding the difference between MCB RCCB and RCBO
Understanding the difference between voltage ELCB and current RCCB operating principles is essential for evaluating their respective advantages and limitations in earth leakage protection applications.
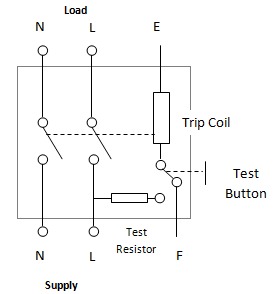
The ELCB operates as a voltage-sensing device connected to the earth wire of the electrical installation. Under normal operating conditions, the earth wire carries no current and remains at zero potential. When earth leakage occurs, current flows through the earth wire, creating a voltage difference that the ELCB detects through its voltage coil mechanism.
The ELCB trip mechanism activates when the detected earth wire voltage exceeds the device's sensitivity threshold, typically set between 50V and 100V. This voltage-based detection method requires a continuous earth wire connection and proper earthing system integrity for reliable operation.
The RCCB operates on the principle of current balance monitoring using a toroidal transformer that encompasses both live and neutral conductors. Under normal conditions, current flowing through the live conductor equals the return current through the neutral conductor, resulting in zero net magnetic flux in the transformer core.
When earth leakage occurs, some current flows to earth instead of returning through the neutral conductor, creating current imbalance. This imbalance produces magnetic flux in the toroidal transformer, inducing voltage in the secondary winding that triggers the trip mechanism. RCCBs can detect imbalances as low as 10mA, providing superior sensitivity compared to voltage-operated ELCBs.
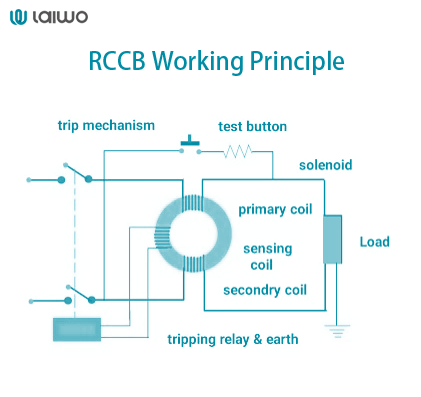
The current-based detection method employed by RCCBs offers several advantages over voltage-based ELCB systems. RCCBs do not depend on earthing system integrity and continue operating effectively even if earth wire connections are compromised. Additionally, RCCBs provide faster response times and greater sensitivity to small leakage currents that may not generate sufficient voltage to trip an ELCB.
The wiring and connection requirements for ELCBs and RCCBs reflect their different operating principles and significantly impact installation complexity and system reliability.
ELCB installations require live, neutral, and earth wire connections, with the earth wire serving a critical role in the device's operation. The ELCB's voltage coil connects between the earth wire and a separate earth electrode, creating a complete circuit for voltage detection. This arrangement makes ELCB operation dependent on continuous earth wire integrity and proper earthing system maintenance.
The complexity of ELCB wiring increases installation costs and creates multiple failure points. If the earth wire becomes disconnected or the earthing system deteriorates, the ELCB may fail to provide adequate protection, potentially creating dangerous situations where earth leakage goes undetected.
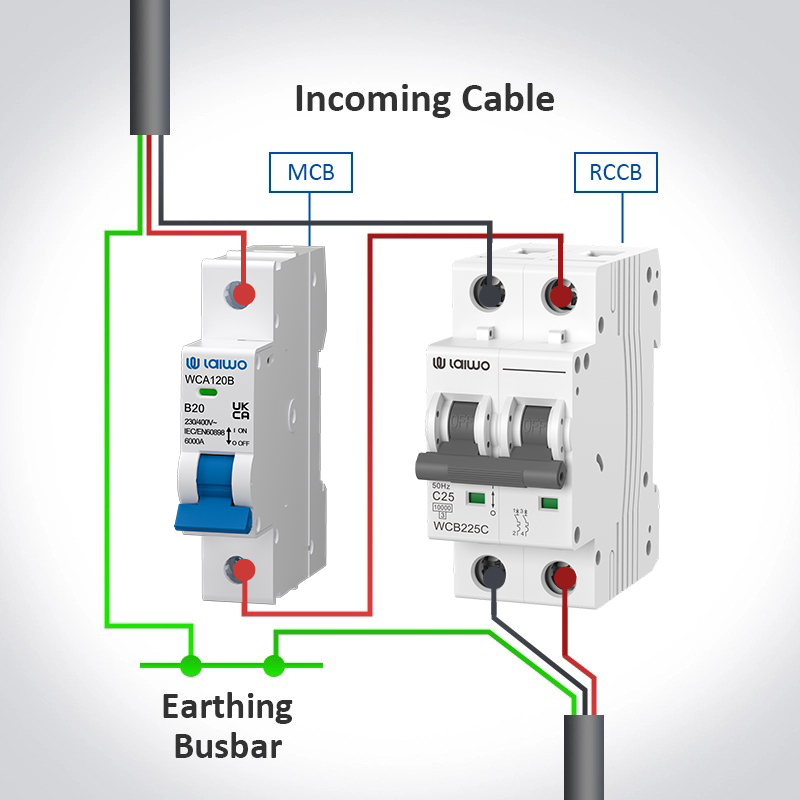
RCCB installations require only live and neutral connections, eliminating dependence on earth wire integrity. The toroidal transformer design allows both conductors to pass through the same magnetic core, enabling current balance monitoring without additional earthing connections. This simplified wiring reduces installation complexity and potential failure points.
The independence from earth wire connections makes RCCBs more reliable in installations where earthing systems may be compromised or where earth wire maintenance is challenging. This advantage particularly benefits industrial installations in harsh environments or older buildings with questionable earthing systems.
When earth wire connections fail, ELCBs become ineffective and may provide false security by remaining in the closed position despite the absence of protection. In contrast, RCCBs continue providing earth leakage protection regardless of earth wire status, maintaining safety even when earthing systems require maintenance or repair.
The sensitivity and response characteristics of ELCBs and RCCBs significantly impact their effectiveness in preventing electrical accidents and ensuring personnel safety in various applications.
ELCBs typically operate with trip voltage thresholds between 50V and 100V, requiring significant earth leakage to generate sufficient voltage for operation. This relatively high threshold may allow dangerous earth leakage currents to persist without triggering protection, particularly in installations with low earth resistance or high earth leakage currents that do not generate adequate voltage.
The response time of ELCBs varies depending on earth leakage magnitude and earthing system characteristics, generally ranging from 0.2 to 0.5 seconds. While adequate for many applications, this response time may be insufficient for preventing electrical shock in high-risk environments.
RCCBs offer superior sensitivity with standard rated residual operating currents of 10mA, 30mA, 100mA, and 300mA, allowing selection based on specific application requirements. The 30mA sensitivity commonly used for personnel protection can detect earth leakage currents well below dangerous levels, providing enhanced safety margins.
Regarding response speed, RCCB trip faster than ELCB in most applications, typically operating within 25-40 milliseconds for rated residual currents. This rapid response significantly reduces the risk of electrical shock and provides superior protection compared to voltage-operated devices.
Learn More: RCCB Tripping Reasons And Fixes
While RCCBs offer superior sensitivity, their high sensitivity may occasionally result in nuisance tripping in installations with naturally high earth leakage currents or electrical noise. Proper selection of RCCB sensitivity ratings and consideration of installation characteristics helps minimize false trips while maintaining adequate protection levels.
ELCBs, while less sensitive, may also experience nuisance tripping due to voltage fluctuations in earthing systems or electromagnetic interference affecting the voltage detection circuit.
The application domains for ELCBs and RCCBs reflect their respective capabilities, limitations, and compliance with modern electrical safety standards.
ELCBs remain present in older electrical installations, particularly in systems installed before modern safety standards adoption. These legacy systems may continue operating adequately in stable environments with well-maintained earthing systems, but require careful evaluation for continued suitability.
Industrial facilities with existing ELCB installations face decisions regarding retrofit timing and cost-benefit analysis of upgrading to modern RCCB-based protection systems. The decision often depends on maintenance requirements, safety compliance needs, and system reliability expectations.
Modern residential, commercial, and industrial electrical installations predominantly specify RCCBs for earth leakage protection due to their superior reliability and compliance with current safety standards. RCCBs serve effectively in diverse applications including:
Residential installations requiring personnel protection (30mA sensitivity)
Commercial buildings with mixed loads and equipment protection needs
Industrial facilities with motor loads and harsh environmental conditions
Outdoor installations where earthing system integrity may vary
Healthcare facilities requiring enhanced electrical safety
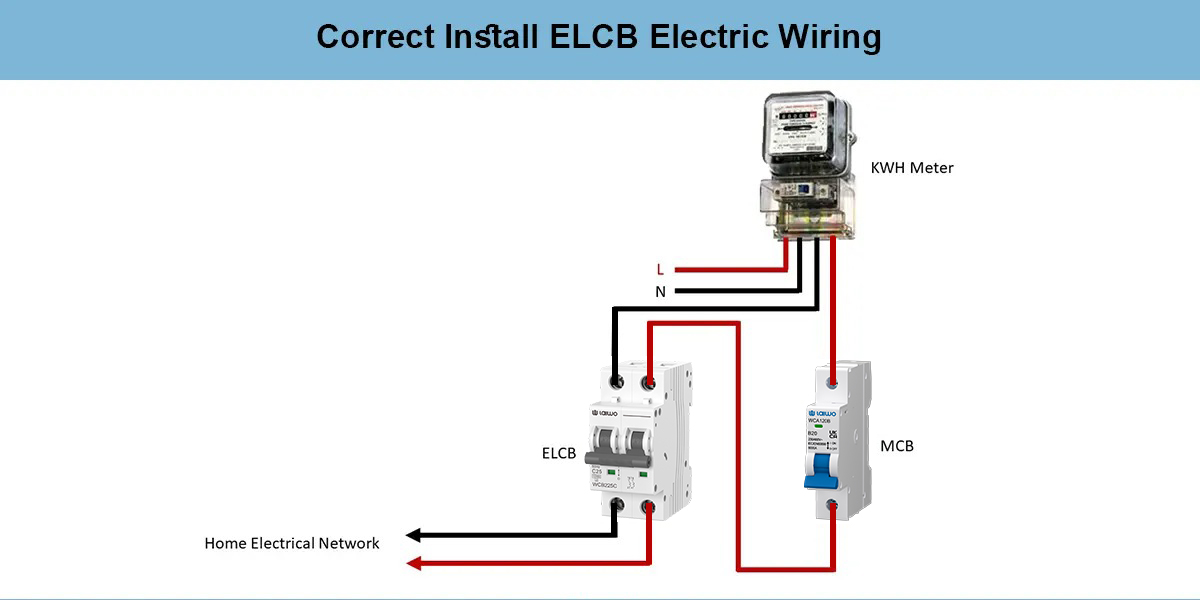
The question can I replace ELCB with RCCB? frequently arises in retrofit projects. Generally, RCCB replacement of ELCBs is possible and recommended, often requiring wiring modifications to accommodate the different connection requirements. The simplified RCCB wiring may actually reduce installation complexity compared to maintaining ELCB earth wire connections.
Specialized applications in moisture-prone areas, such as bathrooms, kitchens, and outdoor installations, particularly benefit from RCCB protection due to enhanced sensitivity and independence from earthing system variations common in wet environments.
A comprehensive comparison of ELCB and RCCB advantages and disadvantages provides essential information for informed procurement and retrofit decisions.
ELCB Advantages:
Lower initial cost compared to quality RCCBs
Simple voltage-based operation principle
Adequate protection in installations with stable earthing systems
Established technology with known characteristics
ELCB Disadvantages:
Dependence on earth wire integrity for reliable operation
Higher trip thresholds may miss dangerous leakage currents
Slower response times compared to modern RCCBs
Non-compliance with current IEC safety standards
Susceptibility to false trips from earthing system voltage variations
RCCB Advantages:
Superior sensitivity with selectable trip currents (10mA-300mA)
Faster response times enhancing personnel safety
Independence from earthing system integrity
Compliance with modern IEC and national safety standards
Simplified installation without earth wire dependence
Better reliability in harsh environmental conditions
RCCB Considerations:
Higher initial cost, offset by improved safety and reliability
Potential for nuisance tripping in installations with high natural leakage
Requires proper sensitivity selection for specific applications
| Feature | ELCB | RCCB | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Detection Method | Voltage-based | Current-based | RCCB |
| Sensitivity | 50-100V threshold | 10-300mA selectable | RCCB |
| Response Time | 200-500ms | 25-40ms | RCCB |
| Earth Wire Dependence | Required | Not required | RCCB |
| Standards Compliance | Outdated | Current IEC standards | RCCB |
| Initial Cost | Lower | Higher | ELCB |
| Long-term Reliability | Limited | Superior | RCCB |
Understanding the regulatory landscape and safety standards governing earth leakage protection devices is crucial for ensuring electrical safety compliance and avoiding legal liabilities in commercial and industrial installations.
Current IEC standards, particularly IEC 61008 (RCCBs) and IEC 61009 (RCBOs), define comprehensive requirements for residual current devices, including performance characteristics, testing procedures, and safety requirements. These standards reflect modern understanding of electrical safety and establish RCCB-based protection as the preferred approach for earth leakage protection.
IEC 60364 installation standards recommend or require RCCB protection in various applications, particularly for circuits supplying socket outlets, outdoor equipment, and installations in locations with increased shock risk. Compliance with these standards often mandates RCCB installation regardless of existing ELCB presence.
ELCBs are largely phased out of modern compliance frameworks due to their inherent limitations and reliability concerns. Most current electrical codes and standards do not recognize voltage-operated ELCBs as adequate earth leakage protection, requiring upgrades to current-operated devices (RCCBs) for compliance.
The obsolescence of ELCB standards reflects documented safety concerns and the availability of superior RCCB technology. Facilities maintaining ELCB-based protection may face compliance issues during safety audits or insurance evaluations.
Modern earth leakage protection devices must meet rigorous certification, testing, and labeling requirements defined by IEC standards and national regulations. RCCBs undergo comprehensive testing including:
Residual operating current verification
Response time measurement
Breaking capacity testing
Environmental endurance testing
Electromagnetic compatibility verification
For B2B buyers, specifying devices with appropriate certifications ensures compliance and reduces liability risks. Quality RCCBs carry CE marking for European markets, UL listing for North American applications, and other national approvals as required.
Making informed decisions between ELCB and RCCB technologies requires evaluating multiple factors including grounding system characteristics, sensitivity requirements, system type, and long-term cost considerations.
Grounding System Evaluation: Assess earthing system integrity and maintenance requirements. Installations with questionable or difficult-to-maintain earthing systems strongly favor RCCB selection due to their independence from earth wire connections.
Sensitivity Requirements: Determine required protection levels based on application risk assessment. Personnel protection typically requires 30mA sensitivity available only with RCCBs, while equipment protection may accept higher thresholds.
System Type Considerations: Residential installations almost universally require RCCB protection for code compliance. Commercial and industrial systems benefit from RCCB reliability and compliance with modern safety standards.
Cost Analysis: While ELCBs may offer lower initial costs, total cost of ownership including maintenance, compliance, and reliability factors typically favors RCCB investment.
Avoiding common mistakes in earth leakage protection selection prevents safety issues and compliance problems:
Continuing to specify ELCBs for new installations due to familiarity or cost concerns
Failing to verify earthing system integrity when maintaining ELCB systems
Selecting inappropriate RCCB sensitivity leading to nuisance tripping or inadequate protection
Ignoring environmental factors affecting device performance and reliability
Overlooking compliance requirements for specific applications or jurisdictions
For procurement managers and electrical engineers, the recommendation is clear: specify RCCBs for all new installations and prioritize ELCB replacement in retrofit projects. The superior safety, reliability, and compliance characteristics of RCCBs justify their higher initial cost through improved long-term value.
When evaluating suppliers, prioritize manufacturers offering comprehensive RCCB ranges with appropriate certifications and technical support. Quality suppliers provide application guidance, helping select optimal sensitivity ratings and device characteristics for specific installations.
The global transition from ELCB to RCCB technology represents a fundamental shift toward more reliable and effective earth leakage protection systems, driven by enhanced safety awareness and technological advancement.
RCCBs and RCDs (Residual Current Devices) have become the universally recognized standard for earth leakage protection, with regulatory authorities worldwide mandating their use in new installations and encouraging retrofit of existing ELCB systems.
This standardization creates opportunities for economies of scale in RCCB manufacturing while driving continued technological improvement and cost reduction. The global market shift also ensures long-term availability of RCCB products and technical support compared to obsolete ELCB technology.
Advanced earth leakage protection technologies build upon proven RCCB principles while adding enhanced capabilities:
Smart Leakage Detection: Integration with building management systems for remote monitoring and diagnostics
Electronic Sensors: Enhanced sensitivity and programmable trip characteristics
Arc Fault Detection: Combined residual current and arc fault protection in single devices
Communication Capabilities: IoT connectivity for predictive maintenance and system optimization
Systematic replacement of ELCB systems with modern RCCBs requires careful planning and phased implementation, particularly in large commercial and industrial facilities. Key considerations include:
Prioritizing high-risk areas and personnel protection circuits
Coordinating with scheduled maintenance to minimize disruption
Training maintenance personnel on RCCB testing and operation
Updating electrical documentation and maintenance procedures
Ensuring adequate spare parts inventory for new RCCB installations
The comparison between ELCB vs RCCB technologies reveals clear advantages favoring RCCB adoption for modern electrical installations. The core differences center on detection methods (voltage vs. current), reliability characteristics, and compliance with current safety standards.
Key Technical Differences: ELCBs operate through voltage-based earth leakage detection requiring earth wire connections, while RCCBs use current-based detection independent of earthing systems. This fundamental difference gives RCCBs superior reliability and broader application suitability.
Performance Advantages: RCCBs provide faster response times (25-40ms vs 200-500ms), higher sensitivity (10-300mA vs 50-100V threshold), and greater reliability in diverse environmental conditions.
Compliance and Standards: Modern electrical codes and IEC standards favor or mandate RCCB protection, while ELCB technology is largely obsolete in current compliance frameworks.
Practical Recommendations: For engineers, buyers, and contractors, the recommendation is to specify RCCBs for all new installations and plan systematic ELCB replacement in existing facilities. The improved safety, reliability, and compliance characteristics justify RCCB investment despite higher initial costs.
Which is better RCCB or ELCB?
RCCB is significantly better than ELCB in terms of sensitivity, response time, reliability, and compliance with modern safety standards. RCCBs provide superior earth leakage protection with faster response (25-40ms vs 200-500ms) and higher sensitivity (10-300mA selectable vs 50-100V threshold). They also operate independently of earthing system integrity, making them more reliable in diverse applications.
Why is ELCB no longer used?
ELCBs are no longer used because they have several critical limitations: dependence on earth wire integrity, slower response times, lower sensitivity, and non-compliance with modern IEC safety standards. Their voltage-based detection method is less reliable than current-based RCCB detection, and most current electrical codes no longer recognize ELCBs as adequate earth leakage protection.
Can I replace ELCB with RCCB?
Yes, you can replace ELCB with RCCB, and it's highly recommended for improved safety and compliance. RCCB replacement typically requires wiring modifications since RCCBs need only live and neutral connections (no earth wire required). This often simplifies the installation compared to maintaining ELCB earth wire connections. Consult with a qualified electrician for proper installation.
Are RCCBs more reliable than ELCBs?
Yes, RCCBs are significantly more reliable than ELCBs. RCCBs don't depend on earthing system integrity and continue protecting even if earth wires are damaged. They offer consistent performance across various environmental conditions and have fewer failure points compared to ELCBs, which require continuous earth wire connectivity for proper operation.
Does ELCB need earthing?
Yes, ELCBs require proper earthing and continuous earth wire connections for operation. The ELCB voltage coil connects between the earth wire and ground electrode, making earthing system integrity critical for device function. If earth wires become disconnected or earthing deteriorates, ELCBs may fail to provide protection. This earthing dependence is a major limitation compared to RCCBs.
The transition from ELCB to RCCB technology represents a significant advancement in electrical safety and protection systems. For procurement managers, electrical engineers, and facility managers, understanding these differences enables informed decisions that prioritize both safety and regulatory compliance while ensuring long-term system reliability and performance.
Learn More:
Breaking Capacity of Circuit Breakers: MCB, RCBO & RCCB Guide
Understanding 1-4 Pole Circuit Breakers: A Comprehensive Guide
RCD vs RCBO: Key Differences in Protection for Modern Distribution Systems
RCBO 6A–40A: B2B Use for Residential & Industrial Circuit Protection
What is the difference between a fuse and a MCB?
What is the difference between a circuit breaker and a circuit protector?
What Is the Difference Between a Circuit Breaker and a Main Switch Disconnector?
INQUIRY NOW