Next: Circuit Breaker Replacement: Key FAQs on Safety, Steps, and Upgrading Amps

The “miniature circuit breaker vs fuse” choice isn’t binary—it’s contextual. Fuses excel in simplicity and niche applications; breakers offer adaptability and cost efficiency. For B2B Procurement Personnel, balancing upfront expenses against lifecycle costs is key. Meanwhile, homeowners eyeing upgrades should prioritize “circuit breaker box” retrofits for safety and scalability.
A fuse is a sacrificial guardian—a thin conductive strip (often housed in a cartridge fuse) that melts under excessive current, severing the circuit. Unlike reusable devices, fuses demand replacement post-failure, a process captured in keywords like “replace circuit breaker fuse.”
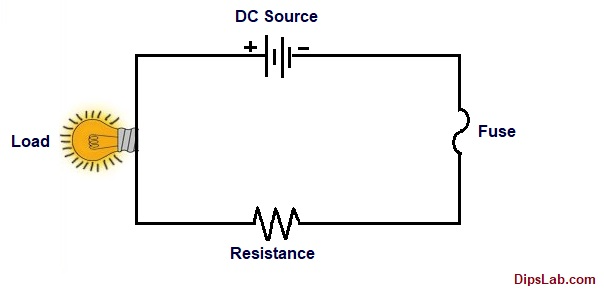
Thermal Response: Overcurrent generates heat, melting the fusible element (e.g., zinc or copper).
One-Time Use: Once blown, the fuse must be replaced—ideal for low-maintenance, cost-sensitive environments.
Automotive Fuses: Blade fuses and automotive fuse circuit breakers protect car electronics.
Residential Systems: Vintage homes rely on fuse box and circuit breaker setups, though modern upgrades favor breakers.
Industrial Cartridges: High-voltage cartridge fuses shield machinery from catastrophic failures.
A circuit breaker is an electromechanical sentinel. Instead of self-destructing, it “trips” a switch during overloads, allowing manual or automatic reset—eliminating the need for replacements.
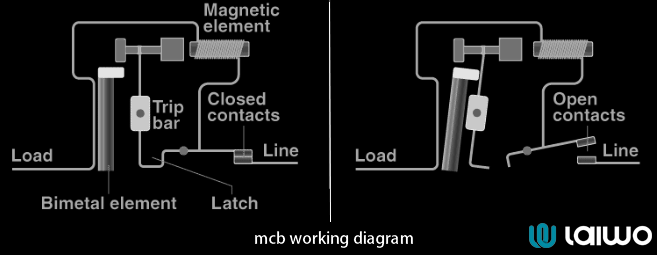
Thermal-Magnetic Tripping: Combines heat-sensitive bimetallic strips (slow response) and electromagnetic coils (instantaneous trip for short circuits).
Resettable Mechanism: Flip a switch to restore power, avoiding the hassle of “replace circuit breaker fuse” scenarios.
Standard Breakers: Protect household circuits (e.g., main power circuit breaker).
GFCI/AFCI Breakers: Prevent shocks and arc faults in modern homes.
Breaker Box vs Fuse Box: Centralized circuit breaker box systems offer scalability and diagnostics, outpacing outdated fuse panels.
Learn More: MCBs Guide: Types, Functions & Electrical Safety Tips
Sacrificial vs Reusable: Fuses melt; breakers trip. The “circuit breaker vs fuse” debate centers on permanence versus convenience.
Response Time: Breakers react faster to short circuits (milliseconds), while fuses vary by design.
Fuse Drawbacks: Replacement risks (e.g., mismatched amperage) and downtime.
Breaker Advantages: Resetting a tripped breaker takes seconds—no need for “how to change a circuit breaker” unless hardware fails.
Upfront Costs: Fuses are cheaper (e.g., 2fora∗∗cartridgefuse∗∗vs2fora∗∗cartridgefuse∗∗vs50+ for a breaker).
Long-Term Economics: Breakers save labor costs over time, critical for enterprises managing “fuse box vs circuit breaker cost” trade-offs.
Fuses: Ideal for automotive systems (car fuse circuit breaker), retrofits, and single-use scenarios.
Breakers: Dominate modern homes, data centers, and industrial grids (circuit breakers vs fuse box compatibility matters here).
Learn More: Understanding the difference between MCB RCCB and RCBO
When investing in electrical protection devices such as MCBs, RCCBs or RCBOs, make sure that you always get help from a reliable manufacturer/supplier such as laiwo. laiwo electrical is a one-stop solution for all your electrical needs including surge protectors, distribution boxes, earth leakage protection devices and switched sockets. If you have additional questions or need assistance, please feel free to contact the customer service team. Give us a call and we'll have a team of professionals answer your questions!
INQUIRY NOW